Are you considering transitioning to an electric vehicle (EV); the pivotal aspect of this ownership lies in and indeed, should be carefully contemplated, the charging infrastructure. Given the abundance of available electric car charging stations, selecting an ideal one for your needs could prove overwhelming. This comprehensive guide delves into an exploration of the different types of EV chargers, their respective connectors and types of EV charging plugs; its purpose is to equip you with knowledge for making informed decisions.
Types of Electric Car Charging Stations
Level 1 Charging Stations
Most electric cars typically include level 1 charging stations as standard; these basic chargers utilize a standard 120-volt wall outlet. Offering a slow charge generally extending the range by about 3-5 miles per hour of charging they are convenient for overnight use at home. However, their functionality does not extend to rapid on-the-go replenishment.
Level 2 Charging Stations
The most common type of EV charging connector types, found in public spaces; workplaces and residential settings particularly are Level 2 charging stations. Operating on a 240-volt outlet: they can augment approximately 10 to 60 miles of range per hour of charging, contingent upon the vehicle and charger specifications. For swift replenishment during daytime hours or amidst running errands: Level Two chargers prove ideal.
DC Fast Charging Stations
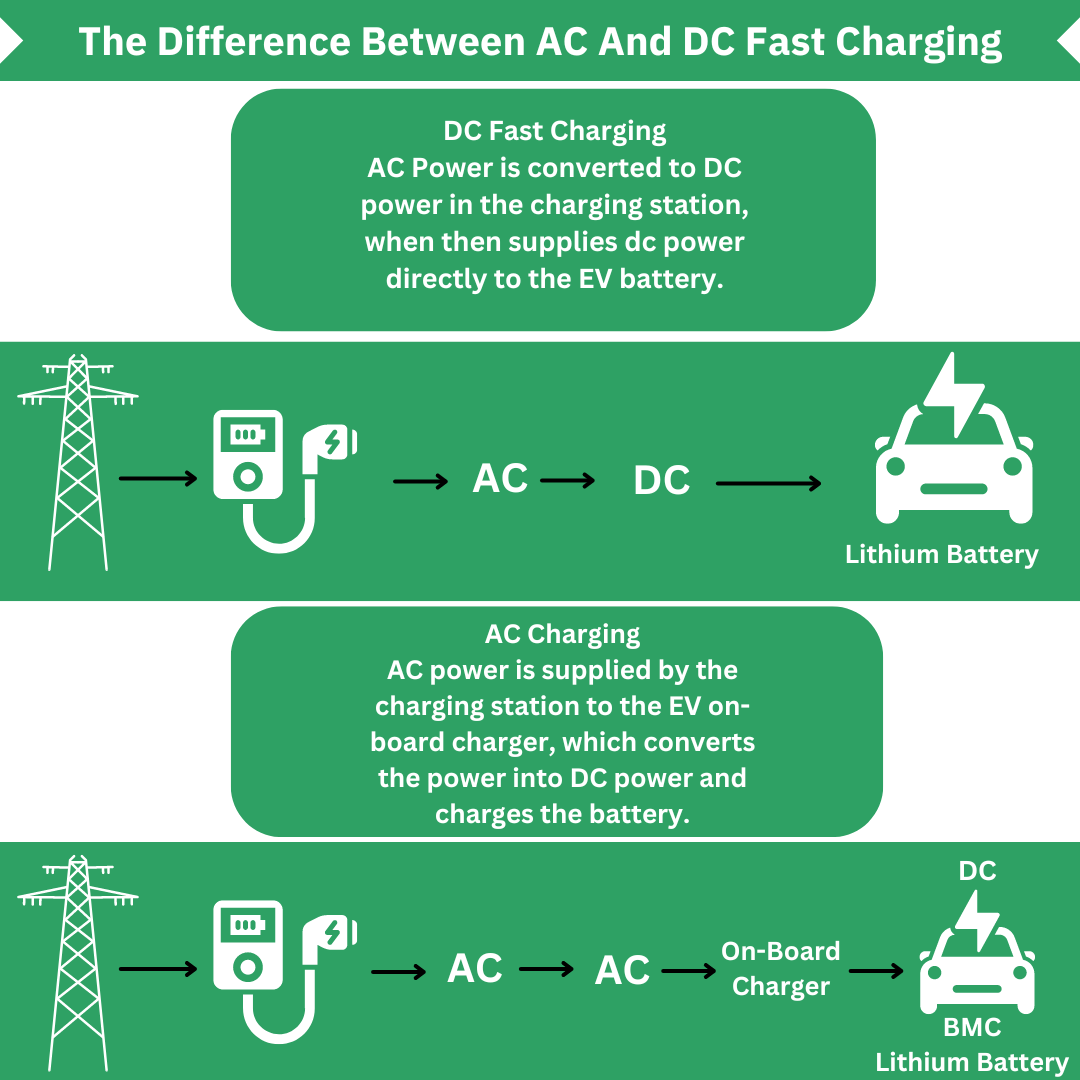
DC fast charging stations, recognized as level 3 chargers; represent the swiftest charging solution for electric vehicles. Capable of delivering up to an 80% charge within a mere 30 minutes: these are optimal options ideal for long trips or rapid top-ups. By implementing a high-powered direct current (DC) connection and circumventing the vehicle’s onboard charger they ensure accelerated charging processes through their DC fast chargers.
Ac Fast Charging Stations
AC fast charging stations, primarily utilized for electric vehicles, provide a more rapid charging solution compared to standard AC outlets. These stations are equipped with higher capacity power outputs, usually ranging from 22 kW to 43 kW, allowing vehicles to charge much quicker—often within a few hours. AC fast chargers are particularly suited for locations where vehicles can park for an extended period, such as shopping centers, office buildings, and residential complexes. While not as fast as DC fast chargers, they offer a balance of speed and accessibility, making them a practical option for daily commuters looking to recharge their EVs efficiently.
Types of EV Chargers Connectors and Plugs
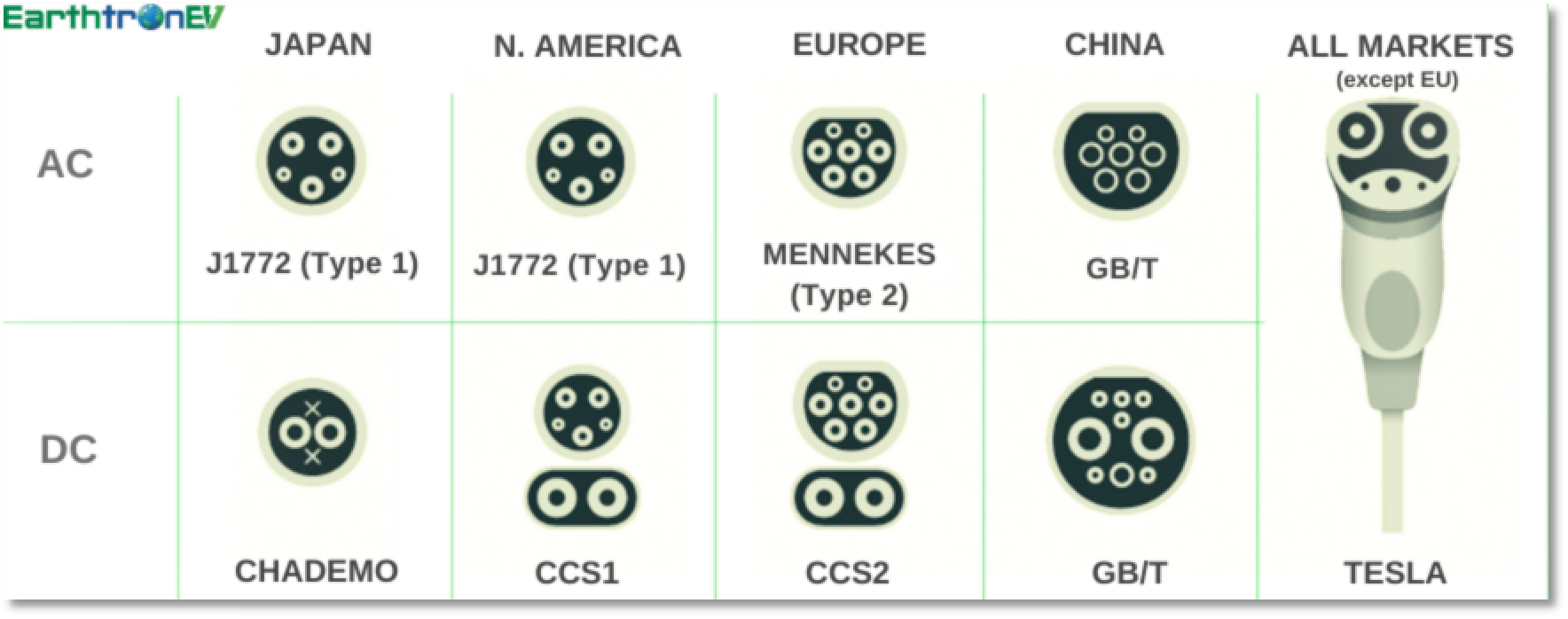
SAE J1772 connector- Type 1
The SAE J1772 connector, also known as the J-plug, is a North American standard for electrical connectors for electric vehicles, maintained by the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE). It facilitates the charging of electric vehicles (EVs) primarily in the United States and Canada. This connector supports both Level 1 and Level 2 charging, offering AC charging capabilities with a voltage range typically between 110 and 240 volts. The design includes a 5-pin configuration: two for power, one for ground, and two for signaling to manage the charging process.

EV connector Type | SAE J1722(Type 1) |
| Output current Type | AC (Alternate Current) |
| <Supply Input | 120 Volts or 208/240 volts (single –phase only) |
| Maximum output Current | 16 Amps(120 volts) 80 Amps (208/240 Volts) |
| Maximum Output Power | 1.92 Kw(120 volts) 19.2 Kw (208/240 volts) |
| EV Charging level(s) | Level1, Level 2 |
| Primary countries | USA, Canada,Japan |
Mennekes connector- Type 2
The Mennekes connector, also known as Type 2, is widely used across Europe for electric vehicle charging. This AC charging standard features a seven-pin design supporting single and three-phase power. It’s recognized for versatility, safety, and compatibility with both public and home charging stations.
The Mennekes connector, commonly known as Type 2, is a standardized electric vehicle charging plug predominantly used in Europe. It features a round shape with a flat top, and can support single-phase or three-phase electrical systems. The Type 2 connector provides a robust and efficient charging solution, offering power levels up to 22 kW in AC mode, and up to 43 kW with DC fast charging. Its design includes safety features such as shutter protection to prevent accidental contact with live parts. The Mennekes Type 2 is widely adopted in public and private EV charging stations across Europe.

| EV connector Type< | Mannekes (Type 2) |
| Output current Type | AC ( Alternate Current) |
| Supply Input | 230 Volts(single phase) or 400 volts phase (three-phase) |
| Maximum output Current | 32 Amps (230 volts) 32 Amps (400 volts) |
| Maximum Output Power | 7.6 kW(230 volts) 22 kW (400 volts) |
| EV Charging level(s) | Level 2 |
| Primary countries | Europe, United Kingdom,Middle East,Africa,Australia |
CCS Connector
European and American automakers widely adopt the Combined Charging System (CCS) connector, a standardized plug that amalgamates AC and DC charging into one.
The Combined Charging System (CCS) connector is a versatile electric vehicle charging standard that supports both AC and DC charging. It combines the Type 2 (Mennekes) connector for AC charging with two additional pins for high-power DC fast charging. CCS connectors are capable of delivering up to 350 kW of power, making them suitable for ultra-fast charging. Widely adopted in Europe and North America, CCS offers compatibility with a broad range of EVs and charging stations. Its design ensures efficient and rapid charging, significantly reducing downtime for electric vehicle users. CCS is a cornerstone of modern EV charging infrastructure.
CCS Connector-Type 1
The CCS (Combined Charging System) Type 1 connector is primarily used in North America for electric vehicle charging. It combines the standard J1772 (Type 1) connector, which handles AC charging, with two additional DC pins for fast charging capabilities. This connector supports high-power DC fast charging up to around 80 kW and AC charging up to 19.2 kW. CCS Type 1 is designed with safety mechanisms to protect users during charging, including robust communication between the vehicle and the charging station to manage power flow. Widely adopted in North America, the CCS Type 1 connector facilitates efficient and rapid charging for a broad range of electric vehicles.
The vehicle and the charging station to manage power flow. Widely adopted in North America, the CCS Type 1 connector facilitates efficient and rapid charging for a broad range of electric vehicles.

| EV Connector Type | CCS 1 |
| Output current Type | DC (Direct Current) |
| Supply Input | 480 volts (three-phase) |
| Maximum Output Current | 500 Amps |
| Maximum Output Power | 360 kW |
| Maximum Output Voltage | 1000 volts DC |
| EV Charging Level(s) | Level 3 (DC Fast charging) |
| Primary Countries | USA, Canada, South Korea |
CCS Connector –Type 2
The CCS (Combined Charging System) Type 2 connector is widely used in Europe and is becoming increasingly common in other regions. It integrates the Type 2 Mennekes connector used for AC charging with additional DC pins for fast charging. This configuration allows for both standard AC charging, typically up to 43 kW, and high-power DC fast charging, capable of reaching up to 350 kW. The CCS Type 2 connector is designed with numerous safety features, including mechanisms that prevent electrical hazards during connection and charging. Its widespread adoption across Europe and in various global markets supports a broad range of electric vehicles, making it a cornerstone of the EV charging infrastructure.
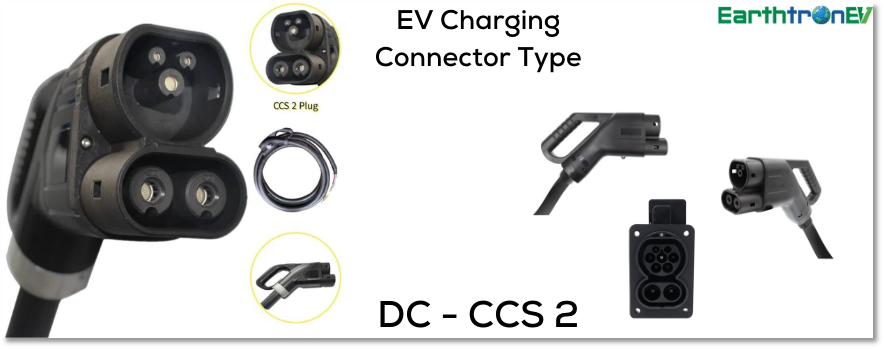
| EV Connector Type | CCS 2 |
| Output current Type | DC (Direct Current) |
| Supply Input | 400 Volts (three-phase) |
| Maximum Output Current | 500 Amps |
| Maximum Output Power | 360 kW |
| Maximum Output Voltage | 1000 volts DC |
| EV Charging Level(s) | Level 3 (DC Fast Charging) |
| Primary Countries | Europe, United Kingdom, Middle East, Africa, Australia |
GB/T connectors
GB/T connectors are the standard for electric vehicle charging in China. They include both AC and DC versions, with the DC capable of high-speed charging. These connectors are known for their distinctive design and safety features, such as insulation and temperature resistance, catering to a vast network of EVs.
GB/T connectors are the standard electric vehicle charging plugs used in China. There are two main types: GB/T AC and GB/T DC. The GB/T AC connector resembles the Type 2 Mennekes but follows a different pin configuration and standard. The GB/T DC connector, distinct with its large and sturdy build, supports high-power fast charging, offering up to 250 kW. These connectors ensure compatibility and safety across China’s EV infrastructure. The GB/T standard facilitates efficient and reliable charging, playing a crucial role in the country’s extensive and rapidly growing electric vehicle market.
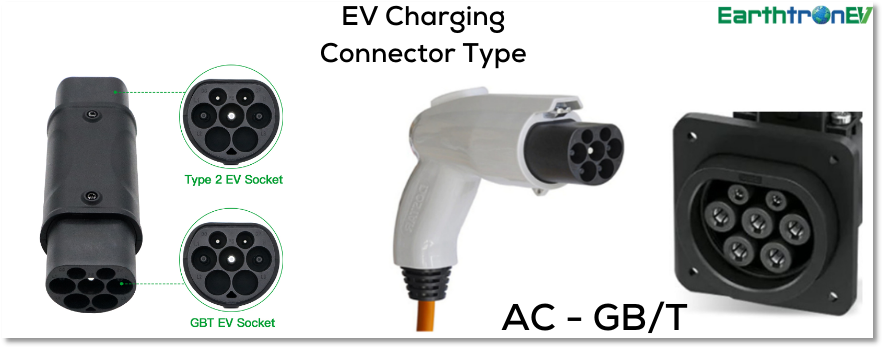

| EV Connector Type | GB/T AC | GB/T DC |
| Output Current Type | AC (Alternate Current) | DC(Direct Current) |
| Supply Input | 250 Volts(three-phase) | 440 Volts |
| Maximum Output Current | 32 Amps | 250 Amps |
| Maximum Output Power | 7.4 kW | 237.5 kW |
| EV Charging Level(s) | Level 2 | Level 3 (DC Fast charging) |
| Primary Countries | China | China |
CHAdeMO Connector
Primarily utilized by Japanese automakers, including Nissan and Mitsubishi, the CHAdeMO connector represents a prevalent form of DC fast charging plug. Equipped with CHAdeMO compatibility, this plug can administer high-powered DC charging to vehicles.
The CHAdeMO connector is a fast-charging standard for electric vehicles developed in Japan. It is designed for high-voltage DC charging, delivering up to 62.5 kW of power, with newer versions supporting up to 400 kW. The connector features a large, round design with multiple pins to handle high currents and communication between the vehicle and charger. Widely adopted globally, especially by Japanese automakers like Nissan and Mitsubishi, CHAdeMO enables rapid charging, typically restoring 80% of battery capacity in 30 minutes. Its robust and reliable design makes it a key player in the fast-charging infrastructure worldwide.
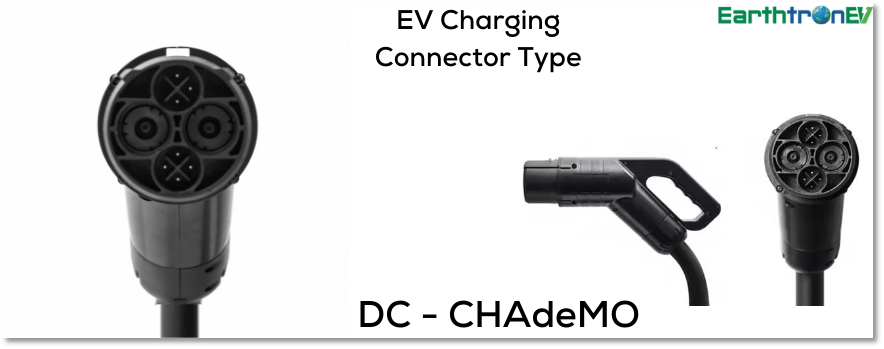
| EV Connector Type | CHAdeMO |
| Output current Type | DC (Direct Current) |
| Supply Input | 400 volts (three-phase) |
| Maximum Output Current | 400 Amps |
| Maximum Output Power | 400 kW |
| EV Charging Level(s) | Level 3 (DC Fast charging) |
| Primary Countries | Japan (older model Evs in use globally) |
Tesla Supercharger Connector
Tesla exclusively utilizes the Tesla Supercharger, a proprietary connector specifically designed for fast-charging their vehicles. However, adapters exist that allow non-Tesla electric vehicles to utilize these specific charging stations.
The Tesla Supercharger connector is a proprietary charging standard developed by Tesla for its electric vehicles. In North America, it features a unique design distinct from other connectors, while in Europe, it uses the CCS Type 2 format for compatibility. Tesla Superchargers deliver high-power DC charging, capable of up to 250 kW, enabling rapid recharging, often adding around 200 miles of range in about 15 minutes. The Supercharger network is extensive, and strategically located to facilitate long-distance travel. This infrastructure, combined with the connector’s high efficiency, underscores Tesla’s commitment to a seamless and fast charging experience for its users.
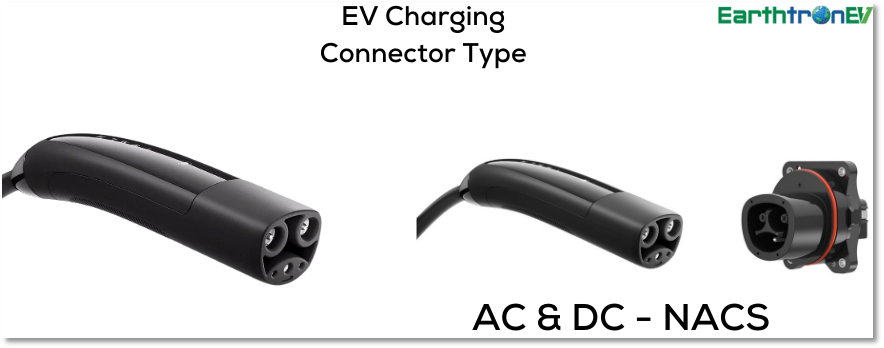
| EV Connector Type | Tesla Nacs |
| Output current Type | AC/DC |
| Supply Input | Single or three phase |
| Maximum Output Current | 48 Amps (AC) 400 Amps (DC) |
| Maximum Output Power | 250 kW |
| EV Charging Level(s) | Level 2/Level 3 |
| Primary Countries | USA, Canada |
Conclusion
To maximize an electric vehicle’s efficiency and convenience, one must make critical choices in the selection of its charging station, EV charger, EV charging connector types and plug. By grasping the available different types of ev charging stations and electric vehicle charging connectors; you can then arm yourself with knowledge to make informed decisions that cater specifically to your unique charging needs. The prospects for future developments in electric vehicle charging are promisingly bright: whether it is a level 1 charger chosen for home use or opting for DC fast-charging on long trips; these options present us with an excitingly rich landscape full of possibilities.
FAQ’s
What does a connection in an EV charger do?
A crucial component in an EV charger, the connection enables communication with the vehicle. Typically, a cable plugs into the EV’s charging port to establish this vital link. Ensuring that it delivers the correct amount of power to the battery is essential; therefore, robust interaction between charger and vehicle becomes imperative. It also allows for monitoring the EV charging connector’s process and managing the battery’s health.
What kind of cable is used to charge EVs?
Known as a charging cable or a EV charging connector types cable, the specialized design of EV-charging cables enables them to manage safely and efficiently the high voltage and current necessary for electric vehicle charges. The Type 2 cable, primarily utilized in AC charging processes, represents one of the most prevalent types among these. Both ends of this cable boast a male connector, plugging into the charging station and the vehicle’s charging port.
Why are there two cords on EV chargers?
Some EV charging connector types feature dual cords: one for AC charging, and another for DC charging; however, as we’ll discuss further below AC charging remains the prevailing and most suitable method. Overnight home or workplace scenarios primarily warrant this type of universal charge a fact you may have already observed. On the other hand, DC fast charging proves significantly quicker and usually serves as a method for rapid on-the-go recharging.
The presence of dual cords on EV charging connector types affords enhanced flexibility in charging options: EV drivers can opt for slower and less costly AC charging or choose faster yet pricier DC fast charging, tailoring their decisions to meet individual needs. The provision of this two-cord system guarantees convenience; it empowers EV owners to charge their vehicles wherever they venture a distinct advantage indeed.